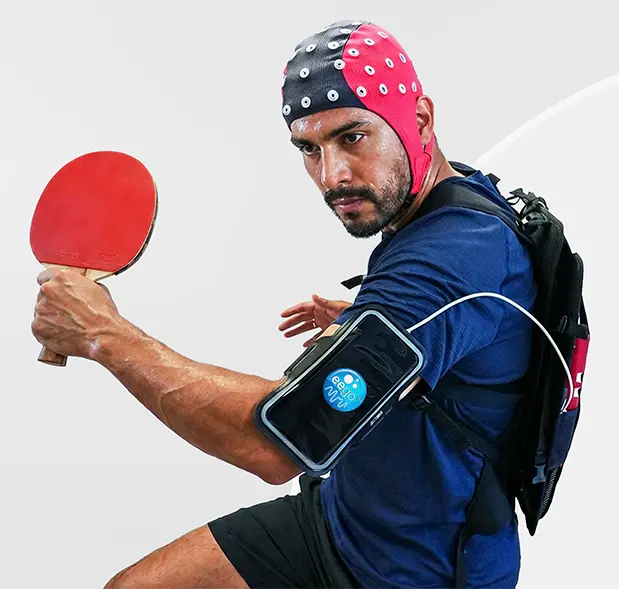
EEG & Mobility
Most research now demands to be done in ecologically valid settings under which subjects can interact with the environment freely through unstructured or semi-structured experiment setups. Anticipating meaningful actions, being able to perform a task in a particular environment, adapting behavior and controlling gait patterns while in a specific environment gives us the singular chance to understand the cognitive control and processes in the brain. Due to its non-invasiveness and high temporal resolution, EEG is a popular neuroimaging method that has been used to investigate brain functions during mobility.
For example, EEG offers the possibility to assess brain function during online walking by correlating cortical activation with gait measures derived from other modalities such as video-based motion analysis devices, inertial sensors and EMGs. Introducing an immersive virtual reality (VR) element in such studies enables users to both investigate brain dynamics in the subject while an environment is perceived as well as during the transition to the environment. Finally, neurorehabilitation measures demand assistive technology devices that are lightweight, portable, non-invasive and ergonomic. Studies show that the combination of EEG and EMG produces beneficial results in active exoskeletons.
Setup Requirements and Technological Challenges
For a mobile EEG recording, subjects need to be able to move around freely without any cabling or hardware restrictions. It therefore helps subject comfort and compliance to the experiment protocol if the EEG equipment chosen is lightweight and portable. Subjects should also be able to carry the full EEG system with them (in a backpack or trolley). Most importantly, the neural signal should be shielded from external noise (50Hz or 60Hz), movement artifacts and electromagnetic interference as much as possible:
Multiple data sources to correlate brain vs. body dynamics
Simultaneous acquisitions help gather multiple sources of information in real time during movement. For example, brain activity (through EEG), behavior (through eye-tracking) and physiology (through ECG) can be extracted from the same subject for a complete investigation. However, many different sources require synchronization between all devices.
The presence of artifacts in the data
There is always a certain trade off to be expected when EEG data is recorded during free movement, line noise and movement artifacts cannot be avoided in such a dataset. Therefore, it helps to incorporate EEG technology that can shield the EEG signal from such artifacts as best possible.
Complexity of real-world learning environments
There are limits on the kind of research questions that can be targeted using mobile neuroimaging, currently, cognitive states are feasible to study while event related research into a specific cognitive process may be harder to investigate.
Technological and data management limitations
The multimodal nature of mobility studies introduces some complexities. For example, incorporating VR has its own limitations such as the absence of a physical body and the presence of a rechargeable battery around the occipital or parietal locations that can introduce some noise into the EEG data. Additionally, the management and storage of data across multiple devices mandates a synchronized recording or storage environment.
Our Solutions
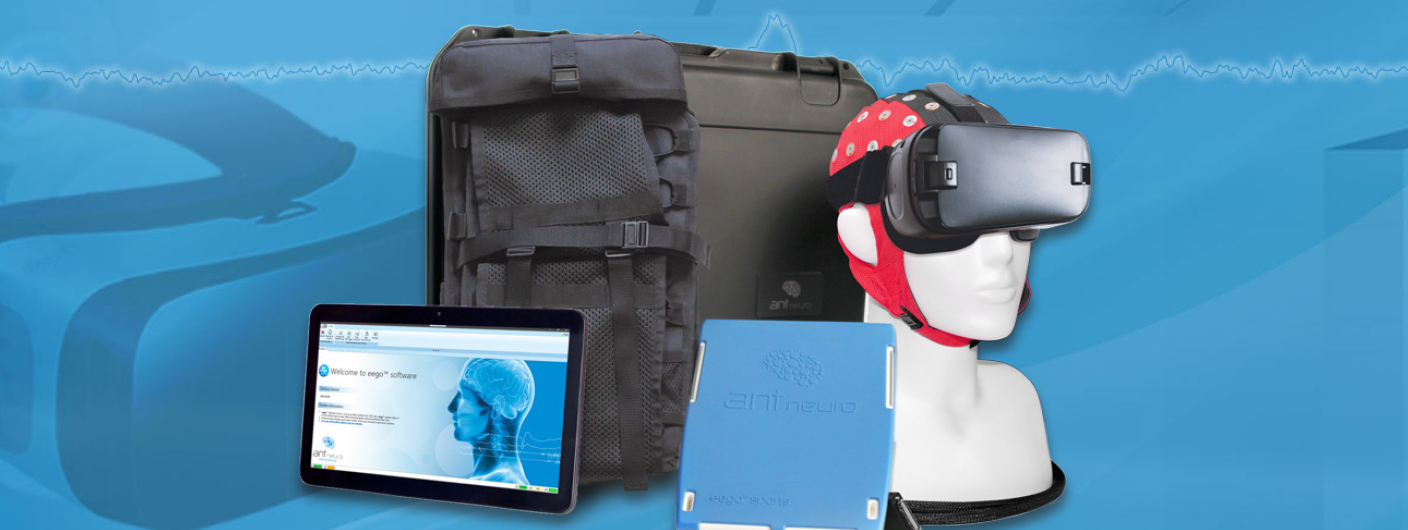
The eego™sports solution is one of our offerings that is very well suited to mobility studies due to the inclusion of the sensor starter kit as well as a backpack onto which all hardware components such as the acquisition tablet and eego amplifier can be loaded.
All bipolar and auxiliary sensor data is synchronized such that sensor data too, is recorded and visualized on the same data view as the EEG channels, removing any need for post-hoc synchronization. While any of the waveguard caps can be chosen in the sports package, we would recommend the waveguard original cap for EEG-VR or similar studies that involve a high degree of physical movement.
Showcases and Publications

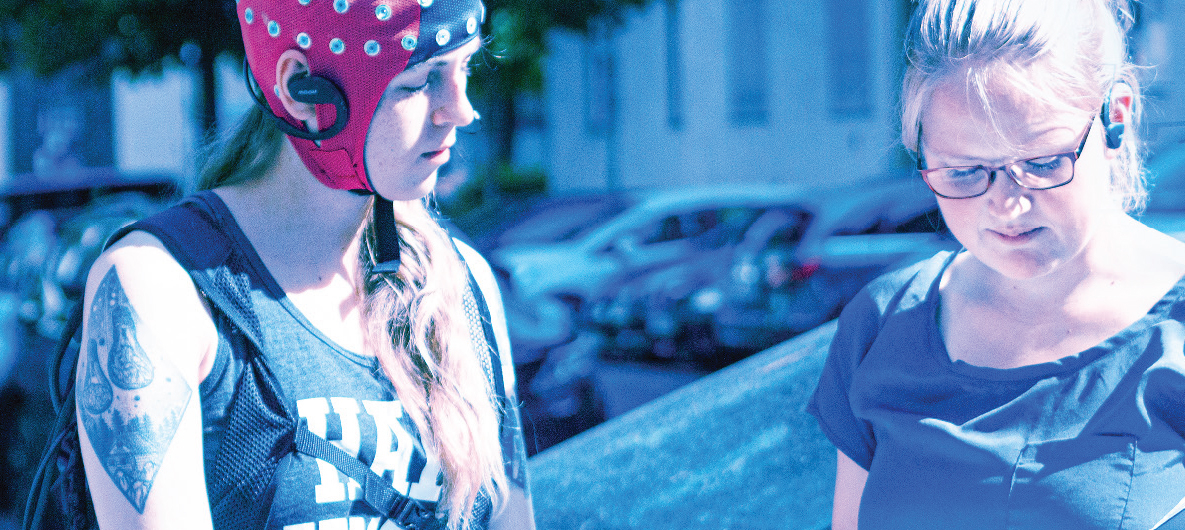
Ultra-mobile EEG & EMG recording solution
Investigating the impact of auditory navigation instructions upon incidental spatial learning in pedestrians.
Read More
The relation between self-paced exercise performance and EEG activity
Influence of hot and hypoxic conditions.
Read More
Simultaneous EEG-VR recordings with your eego™ system
Virtual reality (VR) in combination with simultaneous EEG recordings is increasingly utilized in neuroscience research.
Read More

Cortical oscillations during gait: Wouldn’t walking be so automatic?
Delval, Arnaud, et al.
Read More
The effects of mental fatigue on fine motor performance in humans and its neural network connectivity mechanism: a dart throwing study
Niu, Suoqing, et al.
Read More
Electrocortical evidence for long-term incidental spatial learning through modified navigation instructions
Wunderlich, Anna, and Klaus Gramann.
Read More
