Neurocare: Disorders and Diagnosis
Neuroimaging and neuromodulation are widely used to study neurophysiological processes of various cognitive, social-emotional, motor, and language functions or in the resting state in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Further, neuroimaging and neuromodulation techniques can be utilized for diagnostic purposes, add to a clinical diagnosis, or assess deviations in various functions from the healthy norm compared to a disorder.
For instance, EEG is used to diagnose epilepsy or qEEG can be employed in clinical conditions such as ADHD, schizophrenia, multiple sclerosis (MS), and Parkinson’s disease to compare deviations of ERPs of various paradigms against the norm. TMS is used to e.g. detect the resting motor threshold and motor-evoked potentials which can be associated with the MS disability and e.g. for presurgical mapping of motor and language areas in tumor patients.
Treatment
Nowadays, TMS has been widely used to treat depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia, PTSD, neuropathic pain, motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease, post-stroke disorders, and addictions among various other psychiatric and neurological conditions. Additionally, based on different EEG frequency bands neurofeedback has been applied to improve symptoms of e.g. depression, ADHD, and anxiety disorders.
Setup Requirements and Technological Challenges
EEG experiments to study various functions and associated frequency bands and ERPs require an EEG system consisting of an EEG cap and an amplifier to acquire neural data. For neuromodulation studies or clinical treatment sessions, a TMS system is needed that is supported by neuronavigation which is widely recognized to significantly improve the accuracy of TMS stimulations within and across TMS sessions.
EEG system:
- Suitability for the clinical population: Some clinical populations may require an easy-to-use and fast-applicable EEG cap in a stationary or mobile setup without restrictions in signal quality.
- Synchronicity of behavioral event data with EEG recordings: Clinical studies of various neural functions assessed via paradigms or neural states require time-accurate onsets of events that align with the simultaneously acquired EEG data via TTL-triggers or LSL network events.
- Confounds in EEG data: Clinical subjects may show behavior/symptoms during the recording that impact the EEG data quality. The feature to annotate data allows the integration of this information to be considered in the post-processing pipeline.
- Databases for qEEG: An integrated comprehensive EEG database is needed to evaluate deviations of a clinical condition from the norm.

TMS neuronavigation system:
- Individual brain/head models: Patient-specific MRIs are crucial to ensure the localization of individual targets considering the individual brain anatomy of the patient.
- Multi-modal MRI features: For personalized treatment sessions additional fMRI-based connectivity information can be important to detect the effective stimulation location on the cortex e.g. referring to the “Stanford Protocol“ for personalized targeting for depression treatment is based on the resting-state functional connectivity patterns, which targets the most anticorrelated subregion of DLPFC with sgACC for the treatment.
- High accuracy within and across TMS sessions: For TMS research purposes and clinical treatments it is highly important to deliver the TMS stimulation pulse at the brain region of interest. Therefore, various stimulation target features with feedback that guides the operator to the target area based on the TMS coil location and orientation parameters are crucial to ensure accurate stimulations within and across TMS session(s).
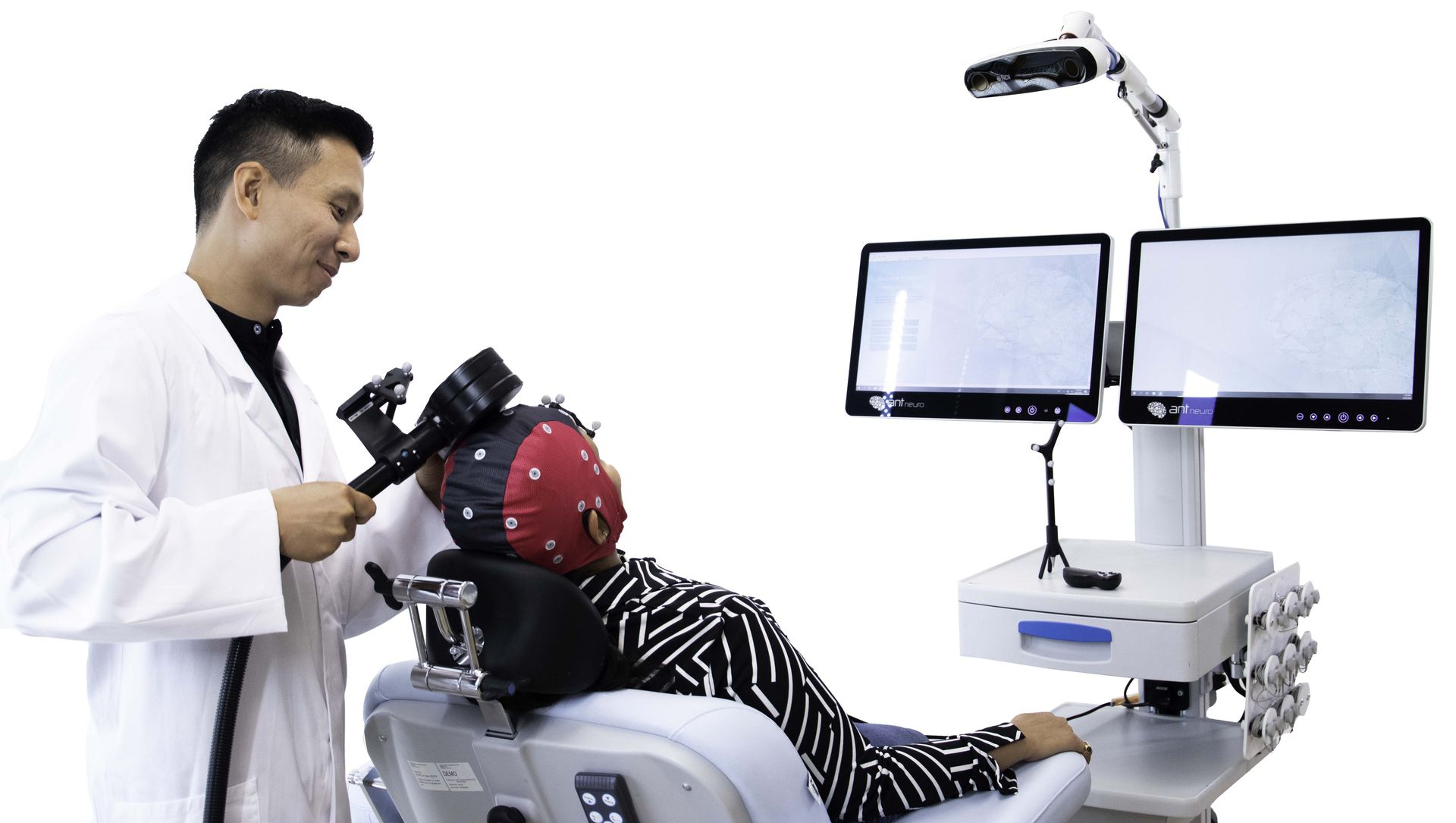
Our Solutions
Based on the challenges, our product range accommodates several product solutions to study and treat associated neural alterations in clinical populations. The eego™ systems combined with a choice of different waveguard™ EEG cap types including gel, dry, and saline solution net caps provide an all-around EEG recording system solution. In combination with our EEG recording system, cognitrace™ adds a range of standard ERP protocols, analysis, and generating qEEG reports. Further, EEG analysis can be conducted with the asa™ EEG analysis software. For neuromodulation studies and treatments, the visor2™ comprises a neuronavigation system compatible with multiple TMS stimulators and coil types from various manufacturers.
Showcases and Publications

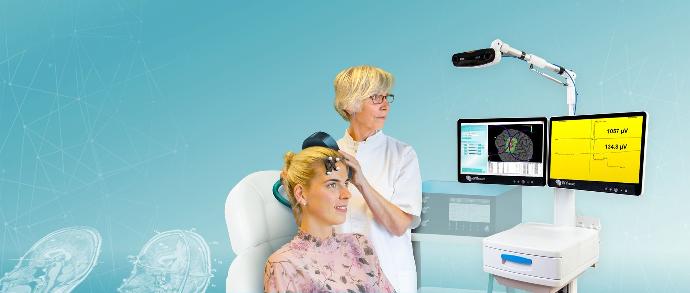
Clinical Application of visor2 for Brain Stimulation
Explore the clinical advantages of visor2 with expert insights from Dr. Rebecca Cohen and Dr. Jordana Hollen of Cohen & Associates.
Read More
Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation of the rostromedial prefrontal cortex in obsessive–compulsive disorder: A randomized clinical trial
Cocchi, L., Naze, S., Robinson, C., Webb, L., Sonkusare, S., Hearne, L. J., Whybird, G., Saffron, G., Scott, G., Hall, C. V., Nott, Z., Adsett, J., Grasby, K. L., Jentjens, J., Scott, J. G., Marcus, L., Savage, E., Zalesky, A., Burgher, B., & Breakspear, M.

Stanford Accelerated Intelligent Neuromodulation Therapy for Treatment-Resistant Depression
Cole, E. J., Stimpson, K. H., Bentzley, B. S., Gulser, M., Cherian, K., Tischler, C., Nejad, R., Pankow, H., Choi, E., Aaron, H., Espil, F. M., Pannu, J., Xiao, X., Duvio, D., Solvason, H. B., Hawkins, J., Guerra, A., Jo, B., Raj, K. S., … Williams, N. R.

Electrophysiological correlates of improved executive function following EEG neurofeedback in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Deiber, M.-P., Ammann, C., Hasler, R., Colin, J., Perroud, N., & Ros, T.



